|
※ INTRODUCTION:
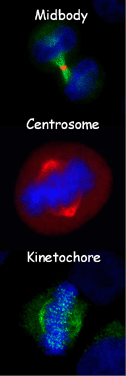
M phase, also called as cell division, is the most crucial and fundamental affair of the eukaryotic cell cycle (Alberts B et al., 2002). After the chromosomes have been replicated during the S phase, the sister chromatids are separated and distributed into two daughter cells equally and faithfully. Also, each daughter cell receives the almost average and necessary intracellular constituents and organelles from the mother cell. Generally, cell division consists of six stages, including prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase and cytokinesis. And the first five stages constituent mitosis (Alberts B et al., 2002). During mitosis, numerous proteins organize protein super-complexes at the three distinct regions of centrosome (Badano JL et al., 2005; Doxsey S et al., 2005a; Doxsey S et al., 2005b; Andersen JS et al., 2003) (spindle pole in budding yeast (Jaspersen SL et al., 2004)), kinetochore/centromere (Chan GK et al., 2005; Fukagawa T et al., 2004; McAinsh AD et al., 2003; Yao X et al., 2000; Yao X et al., 1997; Bloom K et al., 2005) and cleavage furrow/midbody (D'Avino PP et al., 2005; Burgess DR et al., 2005; Glotzer M et al., 2004; Skop AR et al.,2004) (related or homolog structures in plants and budding yeast called as phragmoplast (Otegui MS et al., 2005; Guertin DA et al., 2002) and bud neck (Guertin DA et al., 2002), respectively) spatially and temporally, orchestrating the accomplishment of cell division process.
Although many proteins have been identified to be localized on centrosome, kinetochore and/or midbody, an integrated resource on this area still remains not to be available. In this work, we have collected all proteins identified to be localized on kinetochore, centrosome, and/or midbody from two fungi (Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe) and five animals, including Caenorhabditis elegans, Drosophila melanogaster, Xenopus laevis, Mus musculus and Homo sapiens. From the related literature of PubMed, numerous proteins have been manually curated to be localized on at least one of the sub-cellular localizations of kinetochore, centrosome and midbody. And to promise the quality of data, based on the rationale of "Seeing is believing" (Bloom K et al., 2005), these proteins have been unambiguously observed under fluorescent microscope as directly supportive evidences. Then an integrated and searchable database MiCroKit - Midbody, Centrosome and Kinetochore has been established, implemented in PHP/PERL + MySQL. MiCroKit database is the first integrative resource to pin point most of identified components and related scientific information of midbody, centrosome and kinetochore.
The version 1.0 of MiCroKit database was set up on Nov. 2nd, 2005, containing 1065 unique proteins. The current version 2.0 has been updated on Jun. 5th, 2006, with 1,120 entries. The database will be updated routinely as new microkit proteins are reported. |
 |